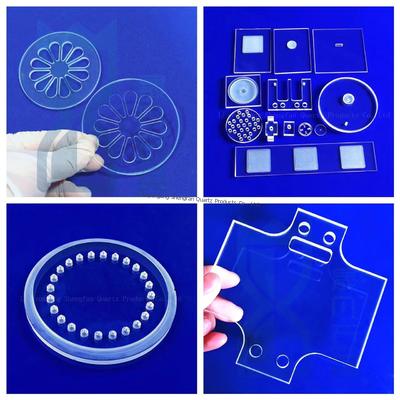
Classification and Use of Quartz Glass Plate
Quartz glass plates, renowned for their high thermal stability and optical clarity, are classified based on material purity and processing techniques, enabling diverse industrial applications
Below are their primary categories and uses:
1. Material Classification
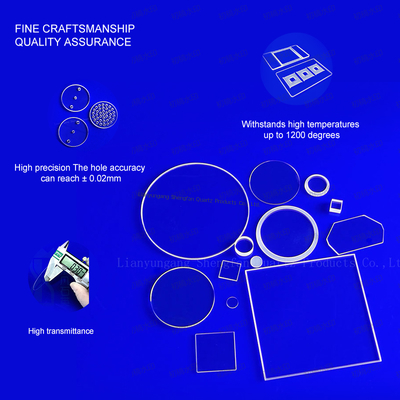
Fused Silica Plates: Composed of ≥99.99% silicon dioxide, these plates offer exceptional UV transparency and resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for semiconductor lithography and laser systems
Borosilicate Quartz Plates: With added boron oxide, these provide enhanced thermal stability at lower costs, suited for laboratory equipment and industrial heating applications
Oxyhalide Tellurite Plates: Specialized for photonic devices, these enable advanced optical filtering and luminescent technologies
Semiconductor Manufacturing: High-purity quartz plates serve as substrates for wafer processing and diffusion chambers, ensuring contamination-free environments. Used as substrates for wafer processing and diffusion chambers, requiring ultra-low metal impurities (<0.5ppm) and thermal stability up to 1200°C
Renewable Energy: Used in solar thermal receivers, these plates withstand extreme temperatures while maintaining optical efficiency
Nuclear Technology: Tested for shock resistance up to 34.5 MPa, quartz plates are employed in reactor observation systems to monitor fuel behavior under high-pressure conditions.
Optoelectronics: UV-transparent plates enable precise light transmission in micro-optical devices, with JGS1-grade material achieving >80% transmittance in 170-2500nm ranges
The quartz glass plate market is experiencing robust growth, fueled by advancements in semiconductor manufacturing and photonic technologies. High-purity quartz plates (≥99.99% SiO₂) are critical for extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography and laser systems

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!