Quartz Glass Tube vs. Borosilicate Glass Tube
1. Basic Definitions & Core Differences
Quartz Glass Tube
Quartz glass tube is made from high-purity fused silica (SiO₂, purity ≥99.9%), produced by melting natural crystal or high-purity silica sand at an ultra-high temperature above 1700°C. It is an industrial specialty glass with nearly single-component composition.
Borosilicate Glass Tube
Borosilicate glass tube is a boron-silicate composite glass, mainly composed of SiO₂ (≈70–80%) and B₂O₃ (≈8–15%), with small amounts of alkali metal oxides (Na₂O, K₂O) and aluminum oxide. It is formed at a melting temperature around 1000–1200°C, belonging to improved alkali-borosilicate glass.
2. Respective Advantages
Advantages of Quartz Glass Tube
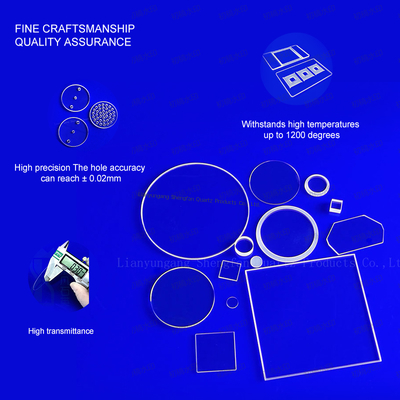
Outstanding thermal stability: With an extremely low thermal expansion coefficient, it can withstand extreme rapid heating and cooling without cracking, and sustains long-term use at high temperatures up to 1100°C, suitable for ultra-high temperature working conditions.
Superior optical performance: It has high transmittance across ultraviolet, visible and near-infrared bands, making it irreplaceable in optical, photoelectric and UV irradiation applications.
Extreme chemical inertness: It is corrosion-resistant to almost all inorganic acids, organic solvents and chemical reagents, only corroded by hydrofluoric acid and hot concentrated phosphoric acid, adapting to harsh corrosive environments.
Excellent electrical properties: It features high volume resistivity, low dielectric constant and dielectric loss, serving as a high-grade insulating material for high-frequency and high-voltage equipment.
High purity: Ultra-low impurity content avoids contaminating high-purity materials in semiconductor, optical and new energy production.
Advantages of Borosilicate Glass Tube
Great cost-performance ratio: Lower production temperature and abundant raw materials lead to a more affordable price than quartz glass, suitable for large-scale daily and industrial applications.
Balanced thermal shock resistance: Although inferior to quartz glass, its thermal shock resistance is far better than ordinary soda-lime glass, meeting rapid temperature change needs in daily and general industrial use.
Stable chemical resistance: It effectively resists acid, alkali and chemical corrosion, satisfying most laboratory, food-contact and conventional chemical processing environments.
Good processability: Easier for cutting, bending, welding and molding, convenient for processing into complex shaped parts (laboratory glassware, pipeline components, etc.).
Safety & versatility: Non-toxic, tasteless and stable, widely used in food contact, medical packaging and daily necessities, with mature processing technology and diversified specifications.
3. Typical Application Scenarios
Quartz Glass Tube
Semiconductor and photovoltaic: High-purity diffusion tubes, furnace tubes, wafer processing components
Photoelectric & optical: UV lamps, mercury lamps, laser tubes, optical fiber preforms, optical lenses
Chemical industry: High-temperature & high-corrosion reaction tubes, pipeline liners, sampling tubes
Metallurgy & analysis: High-temperature furnace tubes, spectral analysis accessories
Medical & environmental: UV disinfection tubes, water treatment UV reactors
Borosilicate Glass Tube
Laboratory glassware: Beakers, flasks, test tubes, condensers, graduated cylinders
Daily use: High-temperature resistant water bottles, coffee cups, baby feeding bottles, baking glassware
Lighting: Energy-saving lamp tubes, explosion-proof lamp shells
Medical & packaging: Ampoules, vials, pharmaceutical packaging
Industrial pipelines: Low-medium temperature corrosive fluid conveying pipes, instrument protective sleeves

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!